Abstract:
Solar flares are intense bursts of energy that originate from the sun and have the potential to affect our technology and infrastructure. This article aims to provide an overview of solar flares, their characteristics, and their effects on Earth. We will also discuss some of the ongoing research in this field, and the measures being taken to mitigate the risks associated with solar flares.
Introduction:
The sun is a massive ball of hot, glowing gas that provides light and heat to the Earth. Occasionally, it releases huge bursts of energy called solar flares. These flares can have significant effects on our planet, including disruptions to our communication and power systems.
Characteristics of Solar Flares:
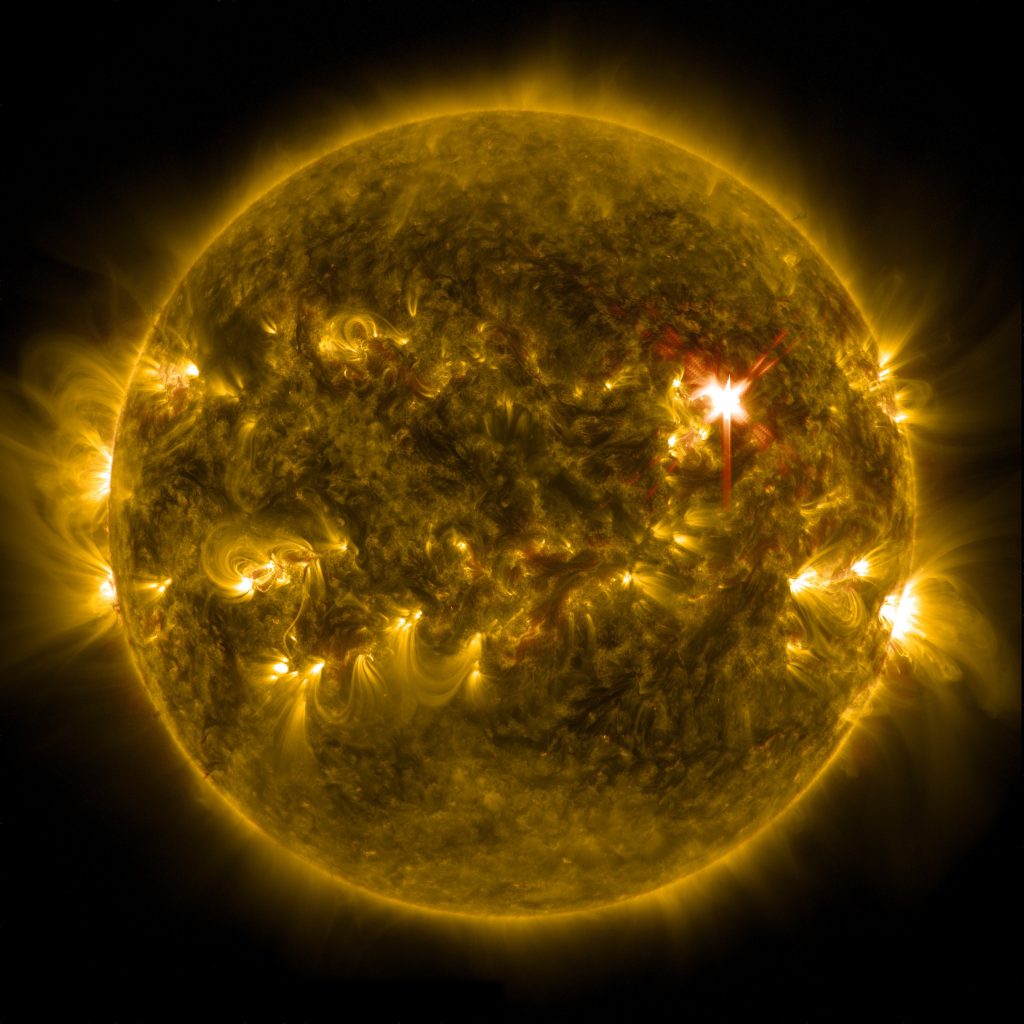
Solar flares are the result of magnetic energy buildup in the sun’s atmosphere. When this energy is released, it produces a sudden and intense burst of radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. The energy released during a solar flare is equivalent to millions of nuclear bombs exploding at once.
The most powerful solar flares are classified as X-class flares, while the weakest are classified as A-class flares. Solar flares are often accompanied by coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which are large clouds of charged particles that can also have an impact on Earth.
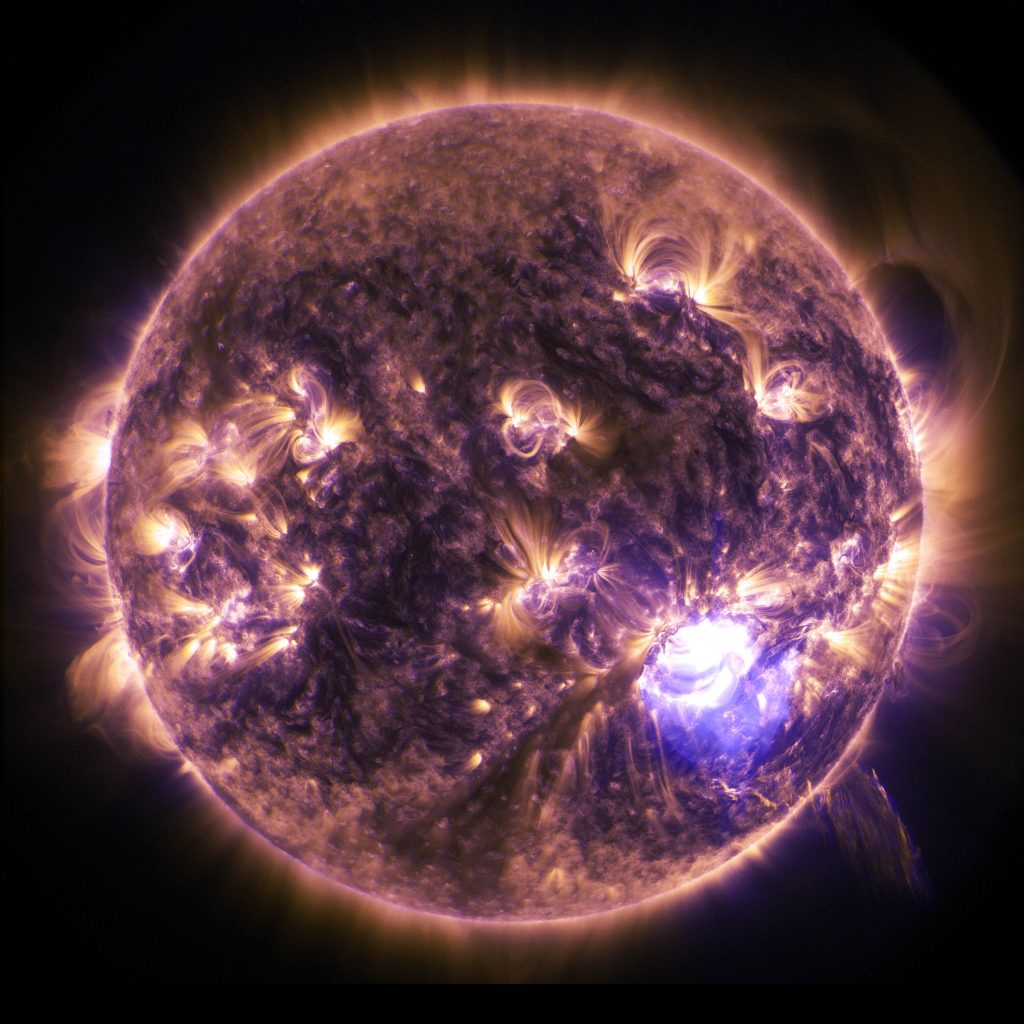

Effects of Solar Flares: Solar flares can have a wide range of effects on Earth, including:
- Communication disruptions: The charged particles emitted during a solar flare can interfere with radio communication and GPS systems.
- Power outages: Solar flares can cause power outages by overloading power grids and transformers.
- Increased radiation exposure: The high-energy particles emitted during a solar flare can be harmful to astronauts and airline passengers.
- Aurora borealis: Solar flares can cause beautiful displays of northern lights, as the charged particles interact with the Earth’s magnetic field.
- Satellites and space missions: Solar flares can damage satellites and disrupt space missions, posing a risk to the safety of astronauts and the success of scientific endeavors.
Research and Mitigation:
Scientists have been studying solar flares for decades in order to better understand their effects and mitigate their risks. This research includes studies of the sun’s magnetic field and its impact on solar flares, as well as efforts to improve our space weather prediction capabilities.
Measures are also being taken to mitigate the risks associated with solar flares. For example, power companies are implementing measures to protect their infrastructure from power surges, while satellite operators are developing more resilient spacecraft.
Conclusion:
Solar flares are a natural phenomenon that can have significant effects on Earth. While these events cannot be predicted with complete accuracy, ongoing research is helping us to better understand and prepare for them. By taking proactive measures, we can reduce the risks associated with solar flares and continue to enjoy the benefits of our sun’s energy.
